2019徐州网络赛补题
B-so easy
B-so easy
参考:2019徐州网络赛 B so easy - binarycopycode - CSDN博客
题目
- 2000ms
- 262144K

大意
有n个点,分别标号为1-n,两种操作:
1 X,表示去掉第X个点2 X,表示查询[x,n]内第一个存在的点。
题解
模拟并查集操作即可(当时并没有想到系列),具体看代码
注意,因为数据量大,所以得用unordered_map代替数组
(unorderd_map的存取查询操作都近似于O(1),map是带log的,而且1e6太大,map会T)
1 | /** |
STL中,
map对应的数据结构是 红黑树。红黑树是一种近似于平衡的二叉查找树,里面的数据是有序的。在红黑树上做查找操作的时间复杂度为O(logN)。而unordered_map对应 哈希表,哈希表的特点就是查找效率高,时间复杂度为常数级别O(1), 而额外空间复杂度则要高出许多。所以对于需要高效率查询的情况,使用unordered_map容器。而如果对内存大小比较敏感或者数据存储要求有序的话,则可以用map容器。
E.XKC’s basketball team
题目
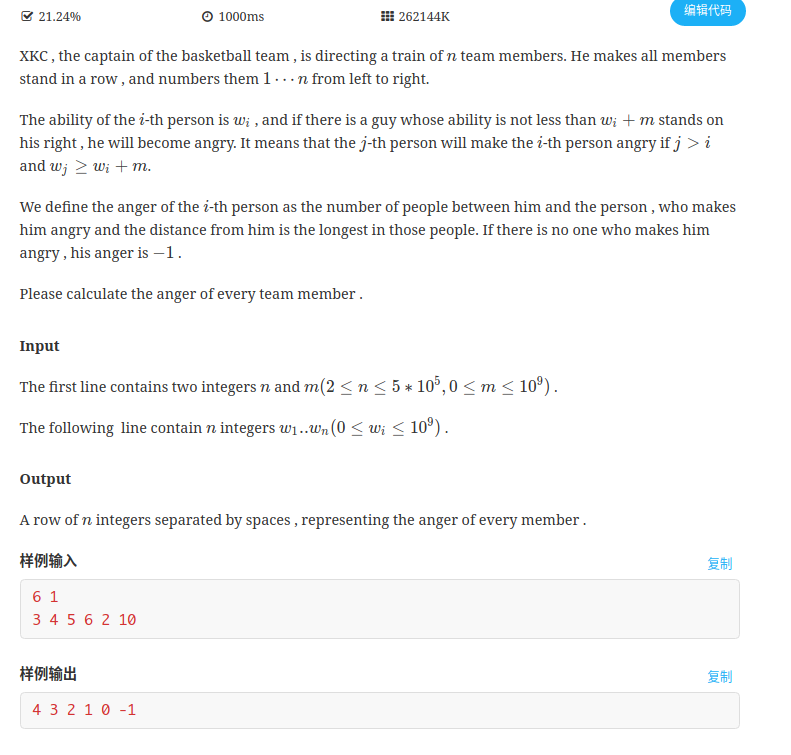
大意
给定n个数,与一个数m,求ai右边最后一个至少比ai大m的数与这个数之间有多少个数
题解
线段树
参考:2019 徐州icpc网络赛 E. XKC’s basketball team - 代码天地
对于每一个数,利用二分的方法求他右边大于等于ai+m的数的最后一个值
关键在于怎么二分呢?
利用线段树存储区间最大值,看这个区间的最大值是不是比ai+m大
1 | /** |
单调队列
从后向前维护一个递增的队列,从后往前遍历:
- 若当前的数大于队尾就进队,否则从该队列中二分找最小的比自己大至少 的数,二者之间的距离即为答案
- 若当前数小于队尾,那这个数一定没有队尾的数优,因为它既比队尾的数靠前,又比它小。
时间复杂度:O(nlogn)
ST表
此题也可以用ST表+二分等方法写出
本博客所有文章除特别声明外,均采用 CC BY-NC-SA 4.0 许可协议。转载请注明来自 GreenHatHGのBlog!
评论