CMU445-Project1-BPlusTree-Insert-Single-threaded
单线程版 B+树插入操作
Overview
- Index: The index in database system is responsible for fast data retrieval without having to search through every row in a database table, providing the basis for both rapid random lookups (快速随机查找) and efficient access of ordered records.
- B+Tree dynamic index structure: It is a balanced tree in which the internal pages direct the search and leaf pages contains actual data entries.
B+ Tree properties
- Each node except root can have a maximum of
Mchildren and at leastceil(M/2)children. - Each node can contain a maximum of
M–1keys and a minimum of ceil(M/2)–1keys. - The root has at least two children and at least one search key.
- While insertion overflow of the node occurs when it contains more than
M–1search key values.
Mis the order of B+ tree. It means every node of that Tree can have a maximum of N children.
For more:
Introduction of B+ Tree - GeeksforGeeksTree Node
举例一个实现后的 b+ tree 如下(p表示page_id):
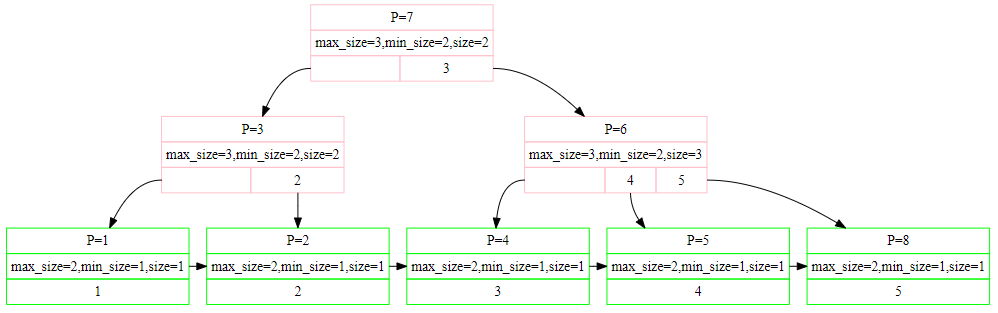
如果是更大的树,则如下图所示: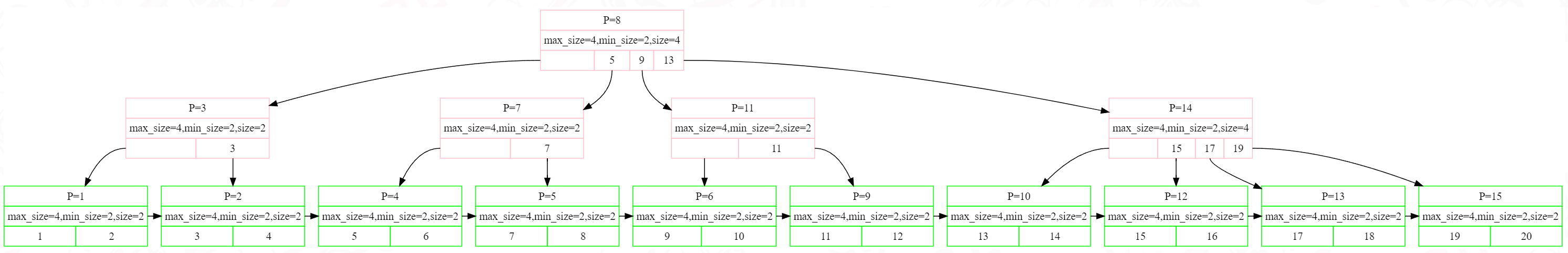
设计思考点:
如果要实现一个 tree,首先得考虑每个节点在内存中是怎么组织的,也就是有哪些关键属性,怎么在内存中管理这些 node。
BufferPoolManager
把 node 再抽象点,其实也不过就是某一块内存数据,在 db 中,内存的管理由BufferPoolManager (bpm) 接管,也就是 lab1 实现的部分。
其管理的单位是 page,也就是每次向 bpm 申请一块内存,返回的都是一个 page,其实在 cpp 中表示就是一个 class Page。
每个 page 的 data_ 大小都是 4096bytes,node 的数据就存放在此。当然 page 还有其他属性,比如 page_id 等,当作 metadata 好管理各个page。1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16static constexpr int BUSTUB_PAGE_SIZE = 4096;
class Page {
public:
Page() { ResetMemory(); }
//...
protected:
static constexpr size_t OFFSET_PAGE_START = 0;
//...
private:
char data_[BUSTUB_PAGE_SIZE]{};
inline void ResetMemory() { memset(data_, OFFSET_PAGE_START, BUSTUB_PAGE_SIZE); }
//...
}
Page
对于 B+Tree 来讲,leaf node 和 internal node 是不一样的,所以这里在 lab 中对应的是 class BPlusTreeInternalPage 和 class BPlusTreeLeafPage,也就是得把从 bpm 申请来的 class Page 中的 data_ 转换为对应 node page。转换的方法是使用 reinterpret_cast:
1
auto *page = reinterpret_cast<InternalPage *>(buffer_pool_manager_->FetchPage(page)->GetData());
这里的意思可以简单理解为:不管你是 InternalPage 还是 LeafPage,实际在代码表示就是一串 byte,这些 bytes 存储在 bpm 的 Page 中,在实际使用中才将其表达为是 InternalPage 还是 LeafPage。
InternalPage 和 LeafPage 都有一个属性
std::pair<KeyType, ValueType> array_- 对 internal node 来讲,这里存储的是 key (search field) 和 child pointer,key 作为一个索引从而能定位到某个 leaf node,child pointer 是为了找到下一级节点。这里 child pointer 其实就是 page_id,因为根据 page_id 能从 bpm 中 fetch 到对应 child page。
- 对于 leaf node 来讲,这里存储的是 key (search field) 和 RID,RID 用于定位实际的 tuple 存放位置。
这两个 node KeyType 都是一样的,但是 ValueType 不一样,page_id 实际类型是 size_t,RID 实际类型是 class RID,所以有
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
class BPlusTreePage {
//...common field
}
INDEX_TEMPLATE_ARGUMENTS
class BPlusTreeInternalPage : public BPlusTreePage {
//...
private:
MappingType array_[1];
}
INDEX_TEMPLATE_ARGUMENTS
class BPlusTreeLeafPage : public BPlusTreePage {
//...
private:
MappingType array_[1];
}
class BPlusTree {
using InternalPage = BPlusTreeInternalPage<KeyType, page_id_t, KeyComparator>;
using LeafPage = BPlusTreeLeafPage<KeyType, ValueType, KeyComparator>;
}
template class BPlusTree<GenericKey<4>, RID, GenericComparator<4>>;
template class BPlusTree<GenericKey<8>, RID, GenericComparator<8>>;
template class BPlusTree<GenericKey<16>, RID, GenericComparator<16>>;
template class BPlusTree<GenericKey<32>, RID, GenericComparator<32>>;
template class BPlusTree<GenericKey<64>, RID, GenericComparator<64>>;class BPlusTree template对应的ValueType是RID,但是InternalPage写的是page_id_t (size_t),并不是直接沿用ValueType。
因为KeyType是自定义类型,所以需要提供一个KeyComparator来定义怎么比对两个Key的大小。
MappingType array_[1];用法是Flexible array,简单来讲就是,当array_写在类属性最后一个时,array_的大小自动指定,不用手动计算,其实就是这样算的:因为一个page是4kb,除去其他属性和元数据的内存开销,剩下的内存全给array_,然后根据array_中每个元素占用多少空间,从而计算出array_size是多少。For more: 做个数据库:2022 CMU15-445 Project2 B+Tree Index - 知乎
从图上可以看到,internal node array_有一个entry中的key是空的,其value指向下一个节点。至于为什么是空的,其实也很好理解,从第二个node起每个都有特定的范围表示,剩下的有没有key都无所谓,因为其表示的范围可以推算出来。所以对于internal node而言,总共有m个key,m+1个value。具体将这个空的key放在左边(本文)或者右边都可以,这会影响到插入、删除、查找等操作。对于leaf node而言,则没有无用的key,每个key和value都是有用的。
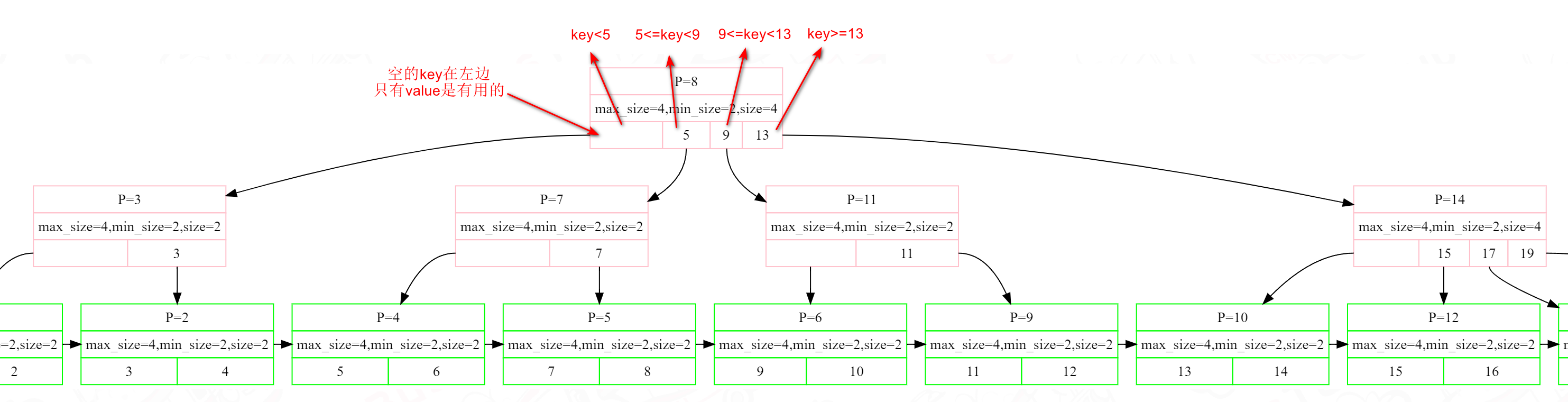
RootPage
每个page都是得经过buffer pool manager拿,这些page再转换成对应的node,每个node之间的关系是通过kv array中的v建立连接,也就是v保存了需要连接的page的page_id。
总有一个开始地方,这个开始的地方就是root_page_id,根据这个page_id可以找到根节点,从而可以找到整棵树,root_page同样也是由buffer pool manager管理。
Find Leaf Node
如何根据一个key找到对应的leaf node呢(key可能在最终找到的leaf node,也可能没有)
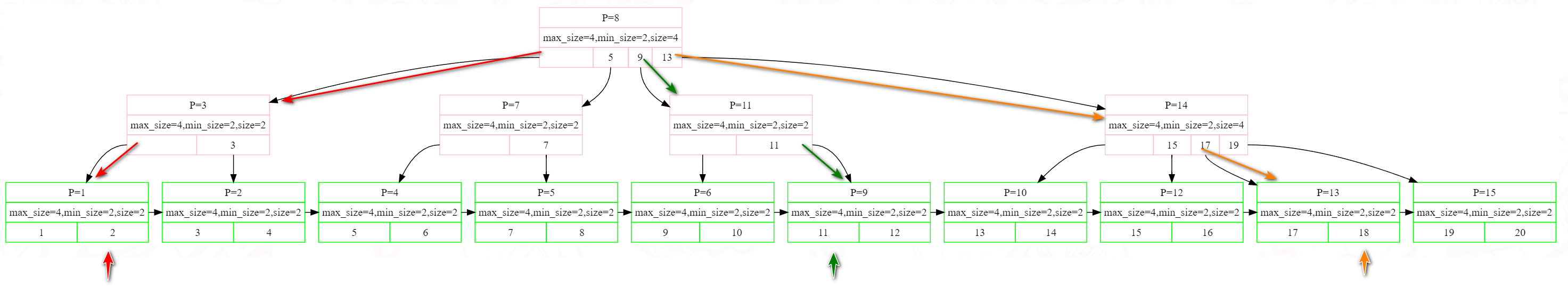
查找部分分为两个,一个是在internal node里面查找,最终定位到leaf node;另外一个是在leaf node中查找有没有这个key。
比如查找11,首先在根节点里面找到对应key,9代表子节点保存的key都符合9<=key<13,那么可以找到9对应的kv,然后根据v是page_id,从buffer pool manager拿到对应的下一个node,也就是p="11的节点。11代表子节点的key都符合key">=11,从而找到P=9的叶子节点,从而在叶子节点找到key=11。
Node Search
不管是在internal node还是leaf node,保存的key都是有序的,所以在node里面查找对应的key可以使用二分算法。
假定要找的值为v,对于internal node来讲,其实就是要找到第一个大于v的key的前一个节点,比如v=11,节点中有5,9,13,那么找到的key是9,因为9这个节点下面所有的key都是大于等于9的。如果没有大于v的key,那么则选择最后一个key。
- internal node查找的过程可以使用upper_bound,其返回指向范围 [first, last) 中首个大于 value 的元素的迭代器,或若找不到这种元素则返回 last。因为这里需要的是前一个节点,所以减去-1就行。因为node的第一个元素key为空,所以这里从第二个元素开始查找。
1
2
3
4auto pair_comparator = [&](const KeyType &val, const MappingType &pair) -> bool {
return comparator(val, pair.first) < 0;
};
return std::upper_bound(array_ + 1, array_ + GetSize(), key, pair_comparator) - array_ - 1;
- internal node查找的过程可以使用upper_bound,其返回指向范围 [first, last) 中首个大于 value 的元素的迭代器,或若找不到这种元素则返回 last。因为这里需要的是前一个节点,所以减去-1就行。因为node的第一个元素key为空,所以这里从第二个元素开始查找。
对于leaf node来讲,可以使用lower_bound,其返回的是第一个大于或等于value的元素迭代器,如果要判断元素是否存在,可判断是否等于value。
1
2
3
4
5auto cmp = [&](const MappingType &element, const KeyType &val) -> bool {
return comparator(element.first, val) < 0;
};
auto idx = std::lower_bound(array_, array_ + GetSize(), key, cmp) - array_;
return idx != GetSize() && comparator(KeyAt(idx), key) == 0;
Tree Search
在树上搜索比较简单,一般是使用一个指针,从root遍历到leaf,需要注意的一点是这个指针类型可能是internal node或者是leaf node。
1 | current = bpm拿到root_page_id对应的page并reinterpret_cast成BPlusTreePage类型; |
需要注意的是记得unpin取出来的page。
Insert
No Overflow
New Root
如果是第一次插入,那么流程就简单点,等于是建树,不过此时树只有一个节点。
1 | if(root_page_id_ == INVALID_PAGE_ID){ |
No New Root
正常情况下的插入的步骤是先根据key找到leaf node,然后在对应的位置(插入后保持key的有序性)插入key和value就行。
这个前提是插入后不发生overflow,对于leaf node,overflow条件是插入后size等于max_size,所以插入前需要判断下size是否小于max_size-1(极端情况下等于max_size-1,插入后size==max_size,就需要overflow了)。
leaf的max_size在初始化BPlusTree时会传入,或者使用默认值。
lab实现的b+树是不能插入重复key的,所以插入前需要判断一下。
常规情况的插入是:
1 | leaf_page = FindLeafNode(key); |
leaf的插入操作一般是:
1 | idx = 使用lower_bound在leaf_page查找应该插入的位置; |
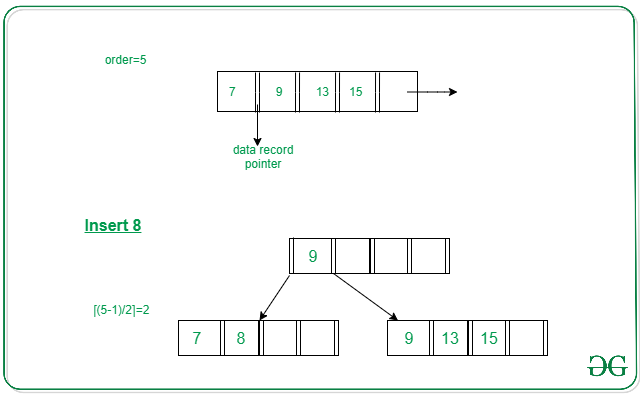
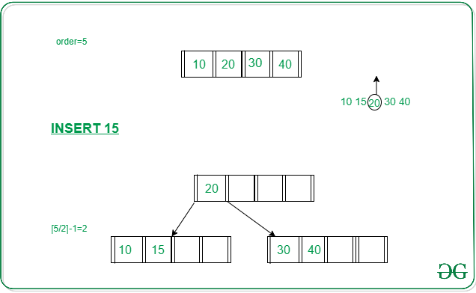
Overflow In Leaf Node
如果插入后leaf node size == max_size就会发生overflow,需要执行split node操作
Leaf Node Is Not The Root Node
如果leaf node不是root node,一般流程如下:
- Split the leaf node into two nodes.
- First node contains ceil((m-1)/2) values.
- Second node contains the remaining values.
- Copy the smallest search key value from second node to the parent node.(Right biased)
example1:
example2:
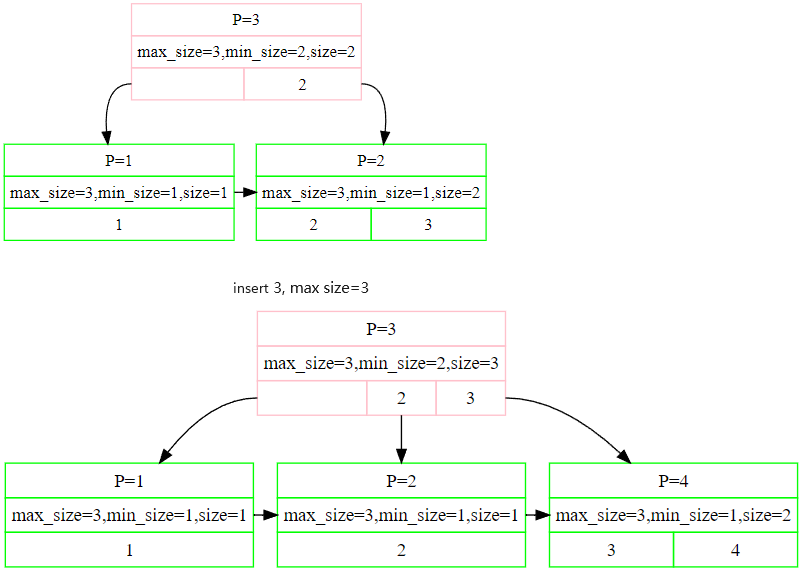
这里的逻辑抽出来就是:
1 | # 已经判断出插入后得发生overflow的前提下 |
Leaf Node Is The Root Node
只有一个root node的时候,这个node的类型其实是leaf node
example1:
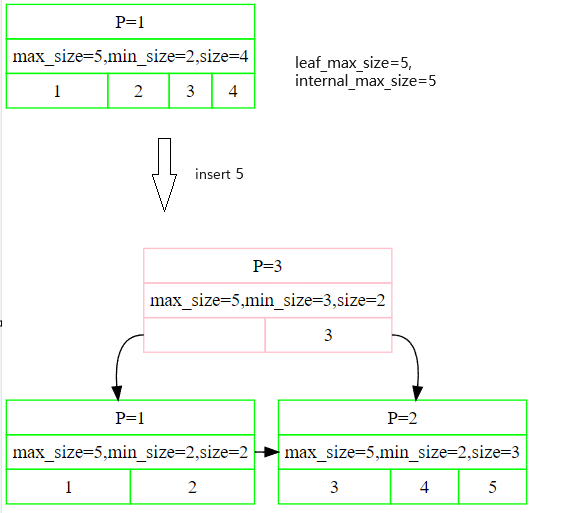
example2:
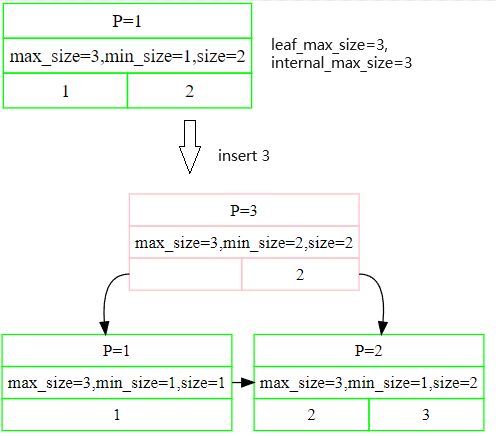
可以看出来,其实和上面的流程有一点类似,只是第四步将smallest kv插到parent这一步不一样,root node节点换了一个,所以流程就是
1 | Split the leaf node into two nodes. |
Overflow In Internal Node
因为需要将smallest kv插入到parent node,所以这里可能会出现的一种情况就是parent node也得spilt。
对于internal node,插入之前的size等于max_size的时候需要拆分,所以这里插入前不拆分的极端情况是max_size-1。流程如下:
Split the non leaf node into two nodes.
First node contains ceil(m/2)-1 values.
Move the smallest among remaining to the parent.
Second node contains the remaining keys.
example1:
example2:
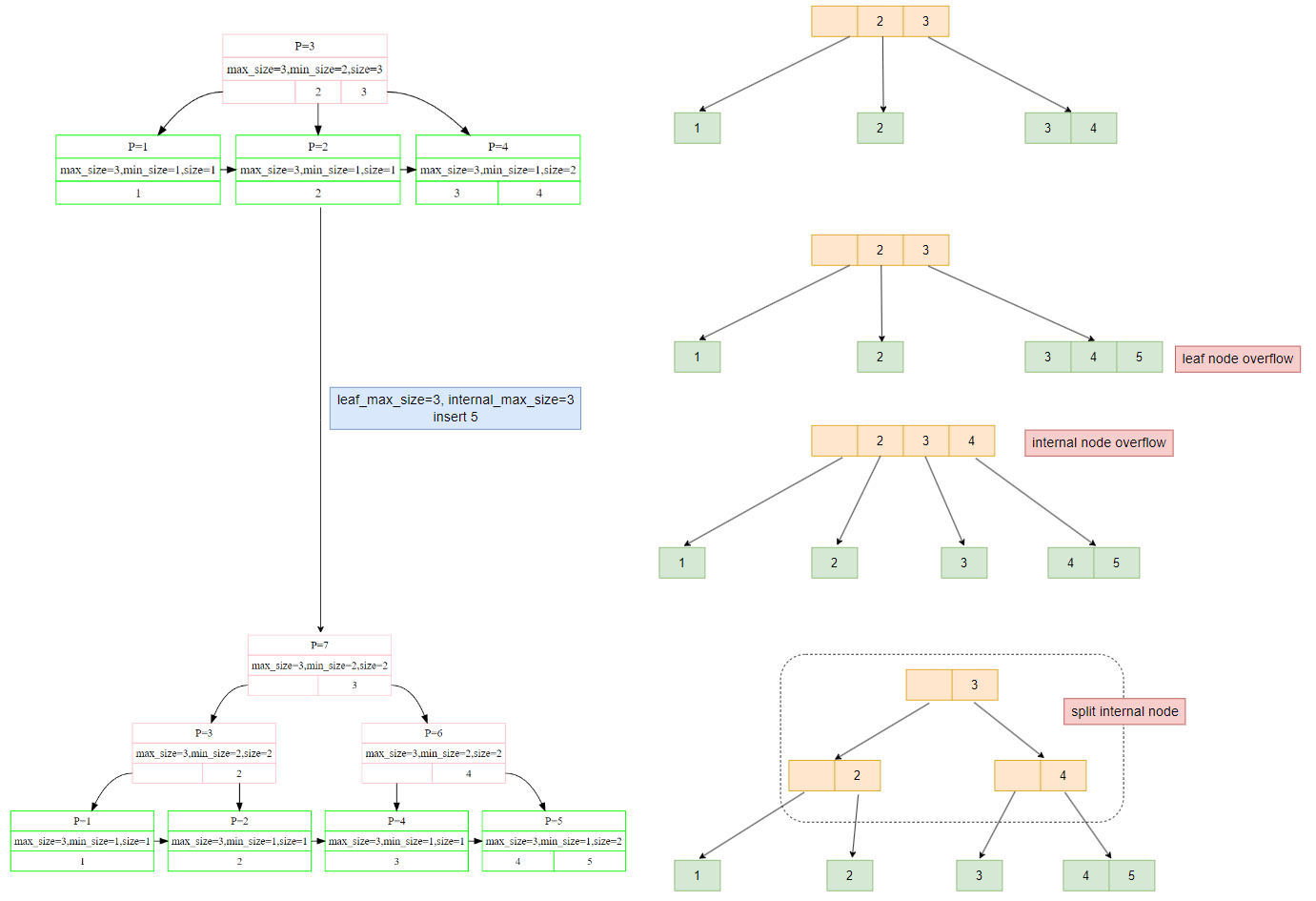
从上面可以看到,insert的时候可能会发生root node节点的变更,从而可能导致重建整个树。
这一块逻辑参考教科书的逻辑即可,比较麻烦,涉及到递归。

递归的逻辑是,如果internal node发生了overflow,向parent node插入key后可能会接着发生overflow,极端情况是一直overflow到root node,然后重建整个树树,这部分的逻辑在上图是insert_in_parent函数里面。
For more:
CMU 15445-2022 P2 B+Tree Insert/Delete - 知乎
CMU 15-445 Project 2 (Spring 2023) | 关于 B+Tree 的十个问题 - 知乎
CMU 15-445 2022 Project2 B+Tree - 知乎