STL之set和multiset
set和multiset容器的操作函数和一道题:HDU 4989 Summary
一、开始
- 使用set或multiset之前,必须加入头文件
- set的含义是集合,它是一个有序的容器,里面的元素都是排序好的,支持插入,删除,查找等操作,就像一个集合一样。所有的操作的都是严格在logn时间之内完成,效率非常高。
set 和multiset容器的内部结构通常由平衡二叉树(balancedbinary tree)来实现。当元素放入容器中时,会按照一定的排序法则自动排序,默认是按照less<>排序规则来排序。两者不同之处在于,multisets允许元素重复,而set不允许重复。
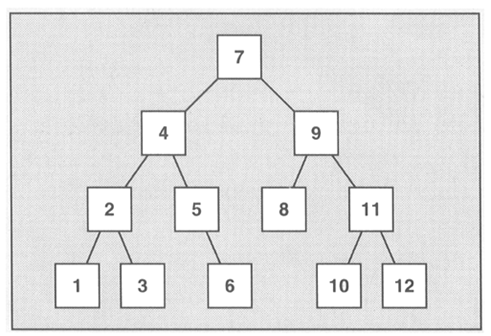
平衡二叉树:
</div>这种自动排序的特性加速了元素查找的过程,但是也带来了一个问题:不可以直接修改set或multiset容器中的元素值,因为这样做就可能违反了元素自动排序的规则。如果你希望修改一个元素的值,必须先删除原有的元素,再插入新的元素。
- sets和multisets具有以下特点:
| Name | Feature |
|---|---|
| set c | 创建一个空的set或multiset容器 |
| set c(op) | 创建一个空的使用op作为排序法则的set或multiset容器 |
| set c1(c2) | 创建一个已存在的set或multiset容器的复制品,容器的类型和所有元素一同复制 |
| set c(beg, end) | 创建一个set或multiset容器,并且以[beg, end)范围中的元素进行初始化 |
| set c(beg, end, op) | 创建一个使用op作为排序法则的set或multiset容器,并且以[beg, end)范围中的元素进行初始化 |
| c.~set() | 容器的析构函数,销毁所有的元素,释放所有的分配内存 |
上面的set可以是下面几种形式:
| Name | Feature |
|---|---|
| set |
以less<>为排序法则的set |
| set |
以op为排序法则的set |
| multiset |
以less<>为排序法则的multiset |
| multiset |
以op为排序法则的multiset |
2. 非变动性操作
| Name | Feature |
|---|---|
| c.size() | 返回当前的元素数量 |
| c.empty () | 判断大小是否为零,等同于0 == size(),效率更高 |
| c.max_size() | 返回能容纳的元素最大数量 |
| c1 == c2 | 判断c1是否等于c2 |
| c1 != c2 | 判断c1是否不等于c2(等同于!(c1==c2)) |
| c1 < c2 | 判断c1是否小于c2 |
| c1 > c2 | 判断c1是否大于c2 |
| c1 <= c2 | 判断c1是否小于等于c2(等同于!(c2<c1)) |
| c1 >= c2 | 判断c1是否大于等于c2 (等同于!(c1<c2)) |
值得注意的是比较操作符只针对相同类型的容器,元素类型和排序法则类型都必须相同。
error例子如下:1
2
3
4
5std::set<float> c1;
std::set< float, std::greater<float> > c2;
...
if(c1 == c2) //error: different types
...
3. 特殊的搜寻函数
sets和multisets在元素快速搜寻方面做了优化设计,提供了特殊的搜寻函数,所以应优先使用这些搜寻函数,可获得对数复杂度,而非STL的线性复杂度。比如在1000个元素搜寻,对数复杂度平均十次,而线性复杂度平均需要500次。
| Name | Feature |
|---|---|
| count (elem) | 返回元素值为elem的个数 |
| find(elem) | 返回元素值为elem的第一个元素,如果没有返回end() |
| lower _bound(elem) | 返回元素值为elem的第一个可安插位置,也就是元素值 >= elem的第一个元素位置 |
| upper _bound (elem) | 返回元素值为elem的最后一个可安插位置,也就是元素值 > elem 的第一个元素位置 |
| equal_range (elem) | 返回elem可安插的第一个位置和最后一个位置,也就是元素值==elem的区间 |
成员函数find()搜寻出与参数值相同的第一个元素,并返回一个迭代器,指向该位置。如果没有找到这样的元素,就返回容器的end()。
下面我们看一个lower_bound(), upper_bound和equal_range(val)例子,或者看博客介绍STL二分法1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
using namespace std;
int main()
{
multiset<int> coll;
coll.insert(1); //插入元素
coll.insert(2);
coll.insert(4);
coll.insert(5);
coll.insert(6);
cout << "lower_bound(3):" << *coll.lower_bound(3) << endl;
cout << "upper_bound(3):" << *coll.upper_bound(3) << endl;
cout << "equal_range(3):" << *coll.equal_range(3).first
<< " " << *coll.equal_range(3).second << endl;
cout << "lower_bound(5):" << *coll.lower_bound(5) << endl;
cout << "upper_bound(5):" << *coll.upper_bound(5) << endl;
cout << "equal_range(5):" << *coll.equal_range(3).first << " "
<< *coll.equal_range(3).second<< endl;
}
程序输出:
lower_bound(3):4
upper_bound(3):4
equal_range(3):4 4
lower_bound(5):5
upper_bound(5):6
equal_range(5):4 4
4. 赋值操作
set和multiset容器只提供最基本的赋值操作:
| Name | Feature |
|---|---|
| c1 = c2 | 把c2的所有元素复制到c1中,同时c1原有的元素被销毁。 |
| c1.swap(c2) | 交换c1和c2的元素。 |
| swap(c1, c2) | 同上,只不过这是一个通用算法。 |
需要注意的是两个容器的类型要一致(包括元素类型和排序法则类型)。
5. 迭代器函数
- sets和multisets的迭代器是双向迭代器,对迭代器操作而言,所有的元素都被视为常数,可以确保你不会人为改变元素值,从而打乱既定顺序,所以无法调用变动性算法,如remove()。
- set和multiset不提供元素直接存取,所以只能采用迭代器
| Name | Feature |
|---|---|
| c.begin() | 返回一个随机存取迭代器,指向第一个元素 |
| c.end() | 返回一个随机存取迭代器,指向最后一个元素的下一个位置 |
| c.rbegin() | 返回一个逆向迭代器,指向逆向迭代的第一个元素 |
| c.rend() | 返回一个逆向迭代器,指向逆向迭代的最后一个元素的下一个位置 |
6. 安插和删除元素
| Name | Feature |
|---|---|
| c.insert(elem) | 插入一个elem副本,返回新元素位置,无论插入成功与否。 |
| c.insert(pos, elem) | 安插一个elem元素副本,返回新元素位置,pos为收索起点,提升插入速度。 |
| c.insert(beg,end) | 将区间[beg,end)所有的元素安插到c,无返回值。 |
| c.erase(elem) | 删除与elem相等的所有元素,返回被移除的元素个数。 |
| c.erase(pos) | 移除迭代器pos所指位置元素,无返回值。 |
| c.erase(beg,end) | 移除区间[beg,end)所有元素,无返回值。 |
| c.clear() | 移除所有元素,将容器清空 |
删除:
1 | auto to_delete = *it; |
7. set实例:
1 |
|
三、一道习题
HDU 4989 Summary
Problem Description
Small W is playing a summary game. Firstly, He takes N numbers. Secondly he takes out every pair of them and add this two numbers, thus he can get N(N - 1)/2 new numbers. Thirdly he deletes the repeated number of the new numbers. Finally he gets the sum of the left numbers. Now small W want you to tell him what is the final sum.
Input
Multi test cases, every case occupies two lines, the first line contain n, then second line contain n numbers a1, a2, ……an separated by exact one space. Process to the end of file.
[Technical Specification]
2 <= n <= 100
-1000000000 <= ai <= 1000000000
Output
For each case, output the final sum.
Sample Input
4
1 2 3 4
2
5 5
Sample Output
25
10
Hint
Firstly small W takes any pair of 1 2 3 4 and add them, he will get 3 4 5 5 6 7. Then he deletes the repeated numbers, he will get 3 4 5 6 7, Finally he gets the sum=3+4+5+6+7=25
代码:1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
using namespace std;
typedef long long ll;
int main()
{
ll sum = 0, arr[110];
int n;
set<int>s;
while(~scanf("%d",&n))
{
s.clear();
for(int i = 0; i < n; i++)
cin >> arr[i];
for(int j = 0;j < n; j++)
for(int k = j + 1; k < n ;k++)
s.insert(arr[k] + arr[j]);
for(auto x : s)
sum += x;
cout << sum << endl;
sum = 0;
}
return 0;
}