CMU445-Project2-BPlusTree-Delete-Single-threaded
单线程版 B+树删除操作
Delete
在删除时用到两个重要的属性是,也就是node最多有多少个search-key value,最少有多少个,根据这个可以决定采用什么措施去维持整个树的平衡
- Each leaf can hold up to
n−1search-key values. We allow leaf nodes to contain as few as⌈(n−1)/2⌉search-key values. - Each nonleaf node in the tree (other than the root) has between
⌈n/2⌉andnchildren.
下面举例课本中的删除过程,粗略了解一下删除的过程:
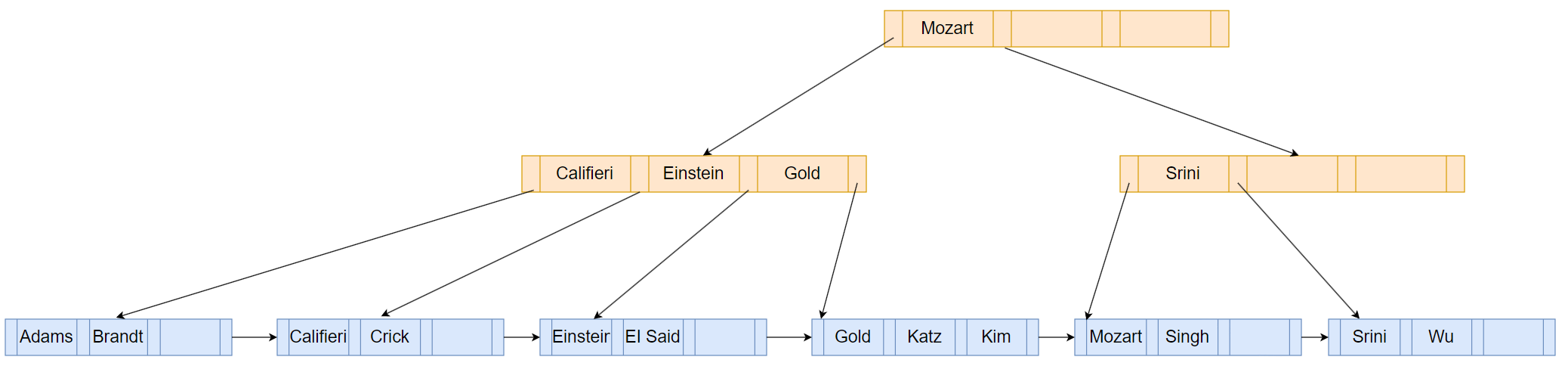
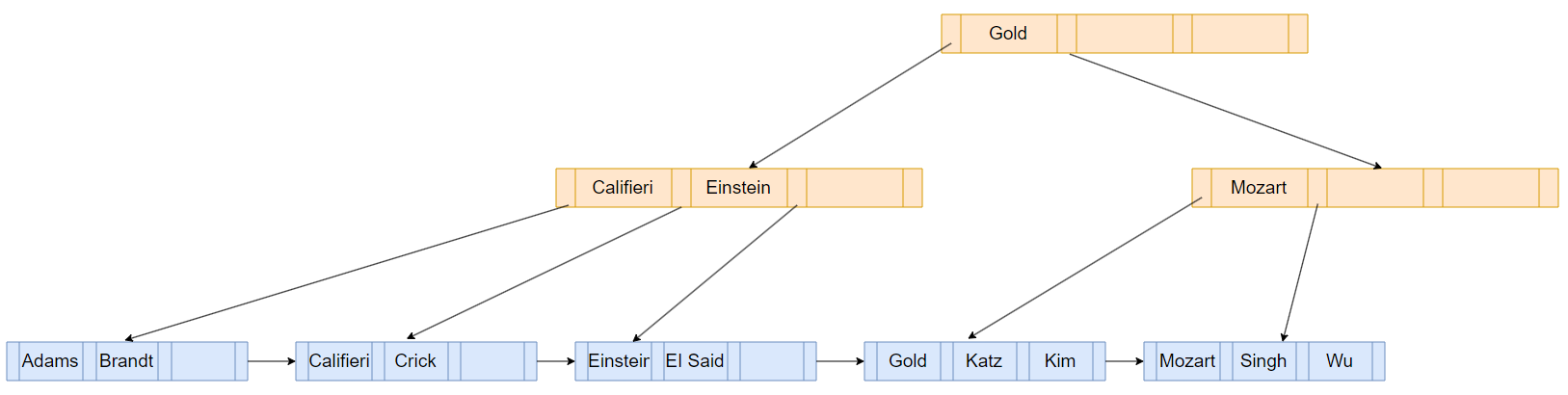
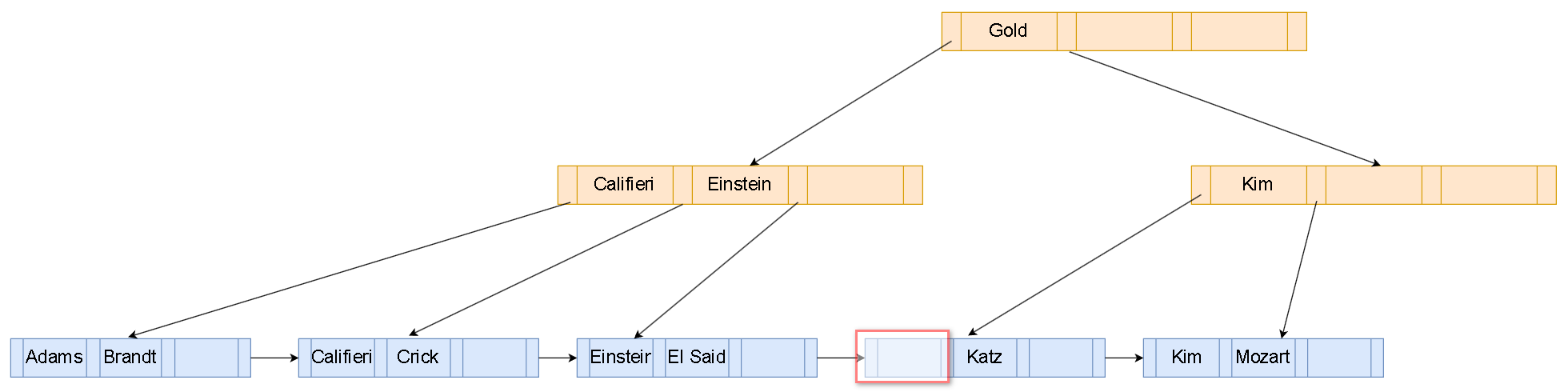
已经有一棵B+树如下,从leaf node可知N=4
所以leaf node最多放3个search-key value,最少2个search-key value;nonleaf node最多4个children,最少2个children。
Coalesce
一开始要删除Srini这个Index,首先查找到Srini位于哪个leaf node,然后将其删除,如下图:
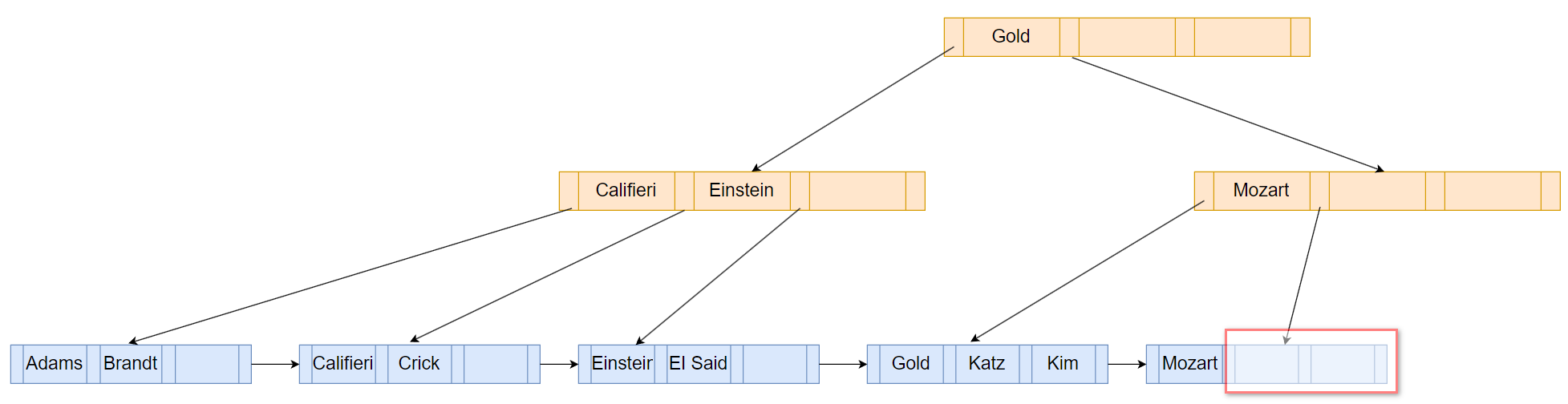
删除后这个leaf node只剩下一个key,不符合树的属性,树的key总共有那么多,为了让每个node都符合上述的属性,有两种方法可以来调整,一个是coalesce,另一个则是redistribute。前者意思是合并兄弟节点,后者意思是节点间重新分配。
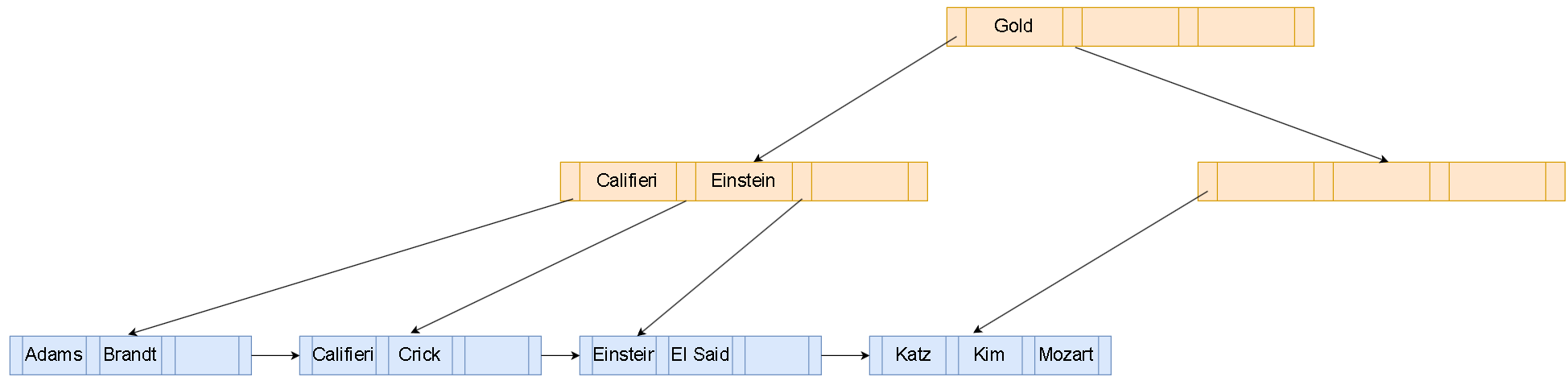
在这里该leaf node可以和左边的兄弟节点合并,然后删除剩下的空leaf node和指向其的parent node
Redistribute
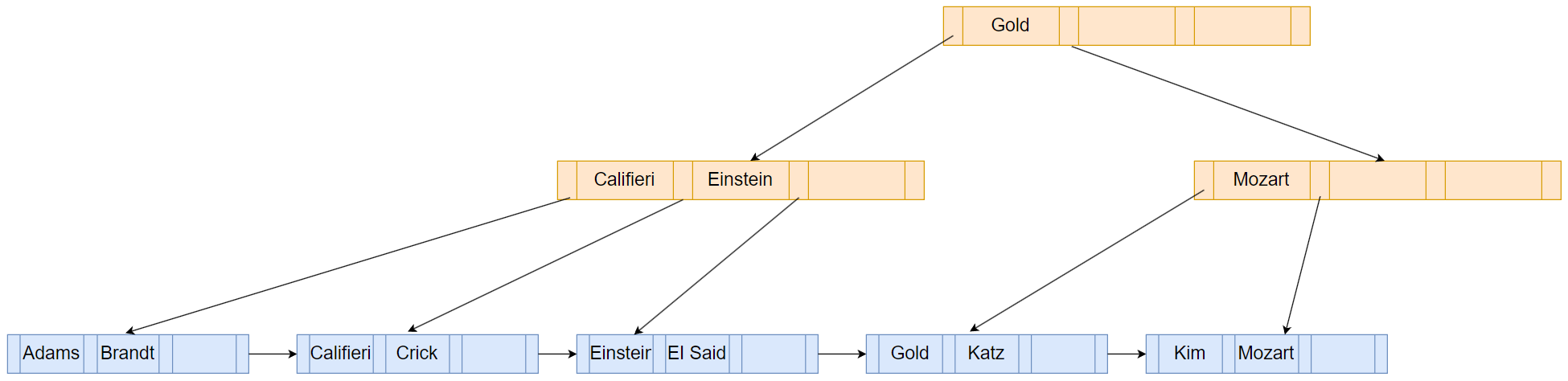
此时有一个internal node(第二层最右边)只有一个entry(key没有用到,value指向下一个节点),不符合树的属性,需要调整。
如果采用合并的策略,那么明显左边的node已经有4个children了,加上现有一个,总共5个,超出最大值。
只能是采取兄弟节点间重新分配的策略,以便每个nonleaf节点至少有2个children
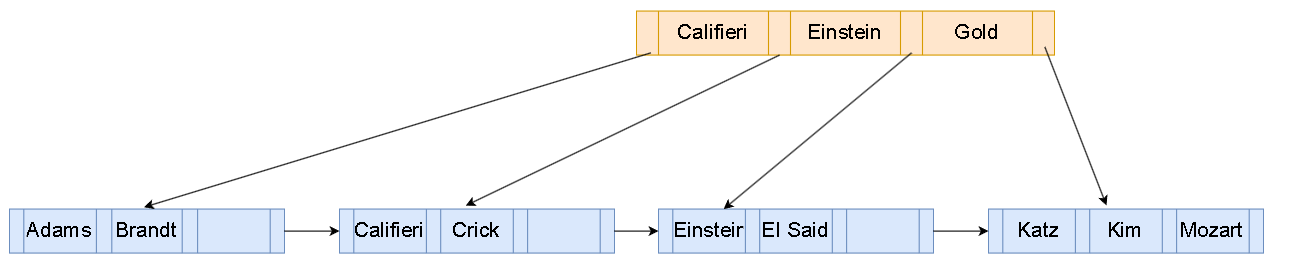
如上图,将左边兄弟节点的Gold search-key移动到右边的节点,此时右边节点共有两个children。此时root节点并不能区分其两个children,因为Mozart左边children的范围应该是小于”Mozart”,右边children的范围应该是大于等于”Mozart”,右边的children不符合要求。所以需要将root节点”Mozart”和children节点”Gold”进行交换,如下图所示。其实也挺好理解的,原本要移动的值是小于其父节点的,现在需要移动到右边,那么肯定不能直接移动,移动了就不符合大小定义了,所以可以直接移动到父节点,而父节点移动到右边,就能满足了,因为整体从左到右是增大的顺序,这样移动保持了相对位置没有发生改变。
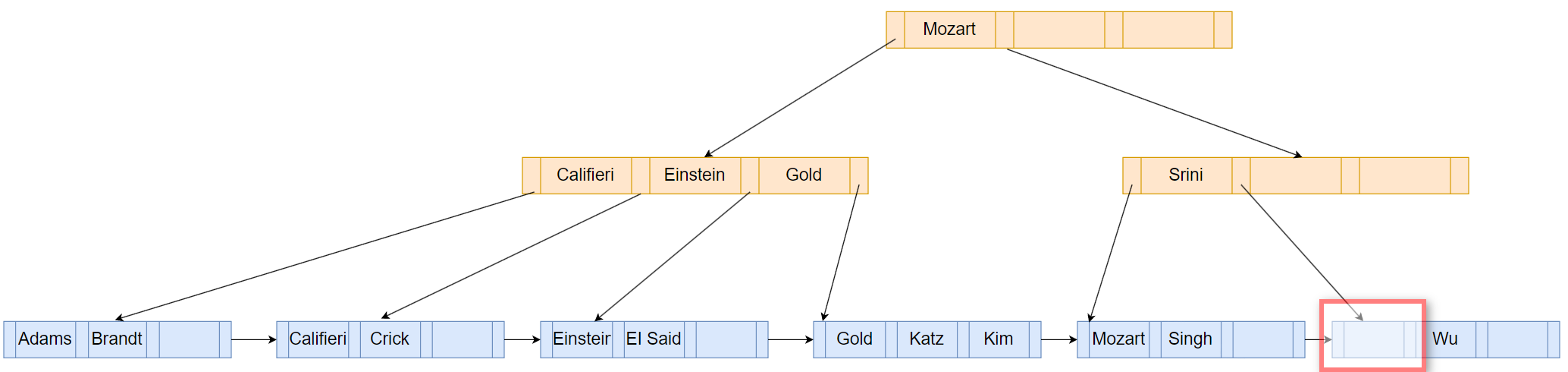
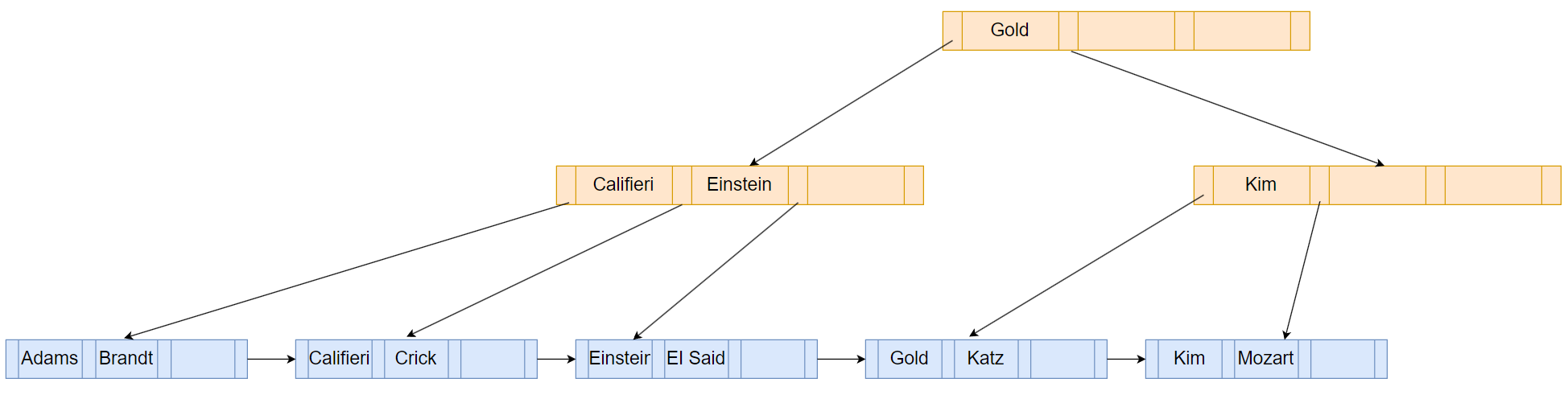
现在接着删除”Singh”和”Wu”,删除”Singh”后还剩下两个search-key value,删除”Wu”后只剩下一个了,该leaf node处于underfull状态。
由上图可知不能合并兄弟节点,只能执行重新分配策略,将左边兄弟节点的”Kim”移动到右边
上图中第二层右边的”Mozart”不能区分其children节点,为此需要将其变成”Kim”,如下图:
Underflow
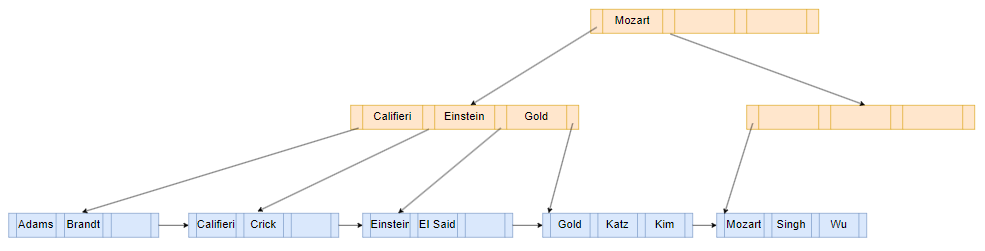
接着删除”Gold”,如下图,该leaf node处于underfull状态
由上图,该leaf node可以和右边的兄弟节点进行合并,同时删除一个parent node:
树中第二层右边那个internal node只有一个children,处于underfill状态,此时可以执行合并或者重新分配策略,用于演示,在书本中选择的是合并。
对于nonleaf node的合并来讲,需要将特定的parent key移动到合并的节点。
这也好理解,因为parent key是区分两个child的关键,现在只剩下一个child了,但是之前的underfill child还有个空的key,但是value有用的item,这个指引功能可以由parent key代替,所以就将parent key移动到合并节点,因为之前得通过parent key能找到那个underfill child,再找到其指向的child,现在underfill child没了,通过parent key直接指引到其指向的child。
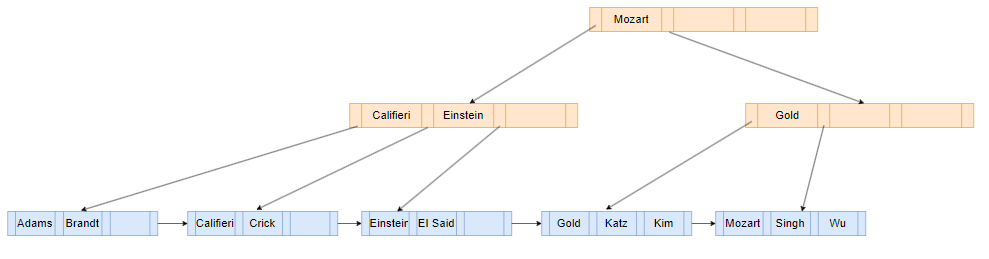
将Gold移动到左边child node,此时root只剩下一个child,但是root至少得两个child,所以root被删除。
需要注意的是,”Gold”从叶子节点中删除了,但是在nonleaf node中还存在。
删除一个节点,可能还需要递归处理其父节点,极端情况下会处理到root节点,调整了整一棵树。
Four Case
上面的流程可以大概知道删除过程什么样
一般来讲可以将删除操作抽象成四个部分:leaf node merge、nonleaf node merge、leaf node redistribute、nonleaf node redistribute
下面的图来自:CMU 15445-2022 P2 B+Tree Insert/Delete - 知乎
Leaf Node Merge
最简单就是叶子节点合并了
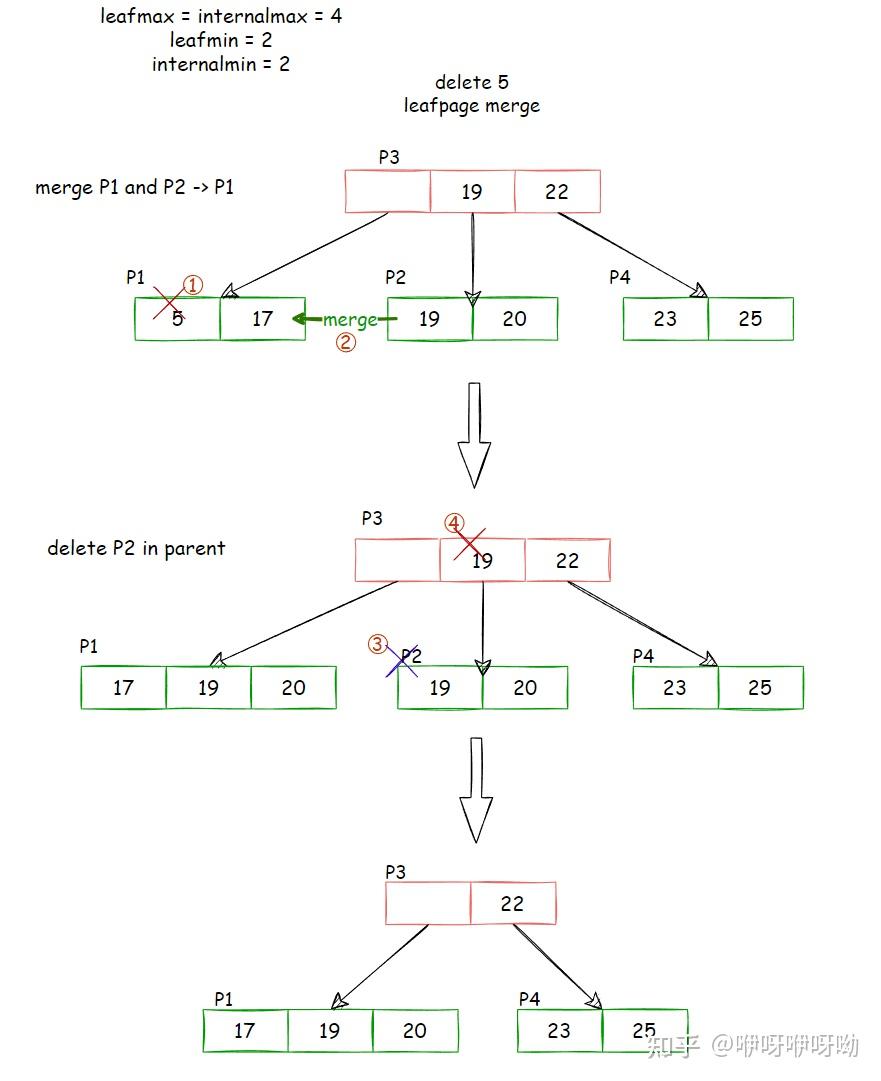
- 删除P1节点的5
- 合并右边兄弟节点P2到P1
- 删除掉P2
- 删除掉指向的P2的节点(P3中的19)
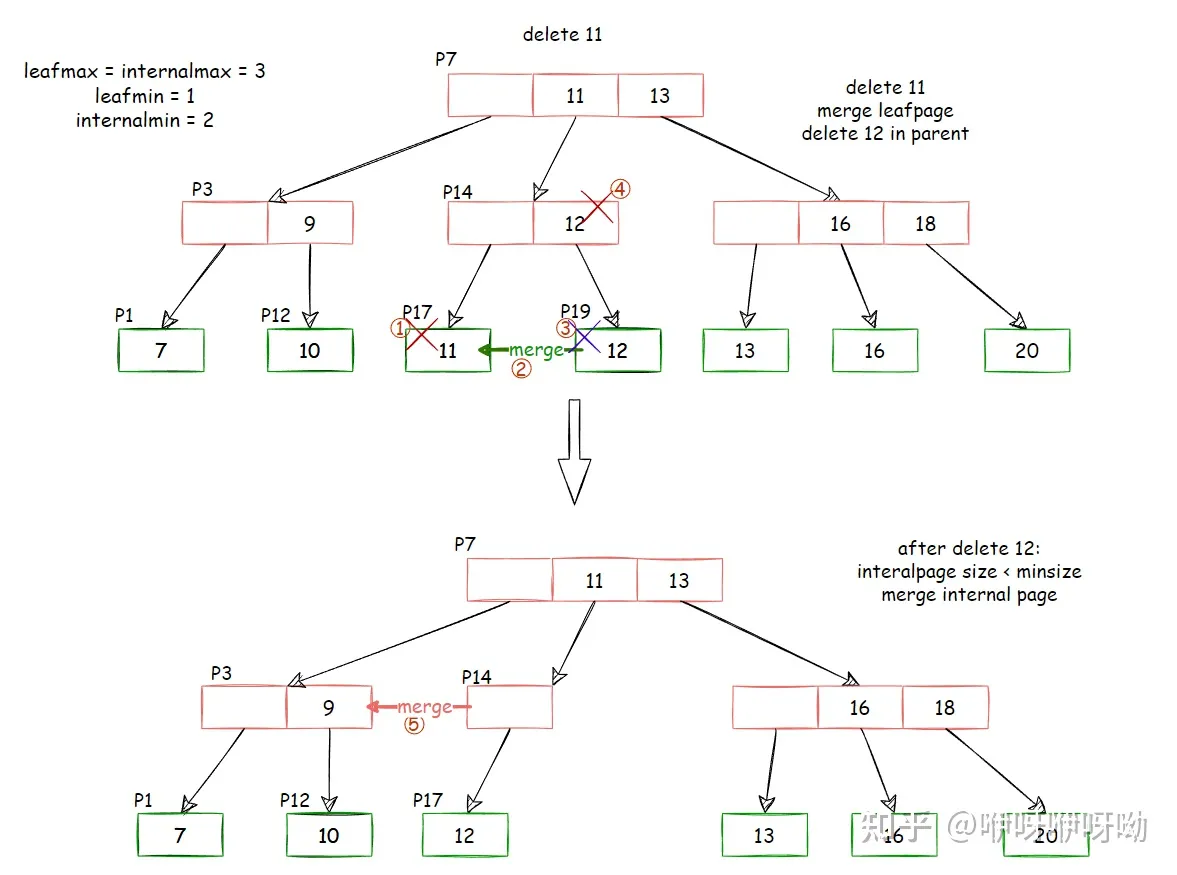
NonLeaf Node Merge
- 删除掉P17中的11
- 删除掉11后,不满足容量最少为1的条件,需要合并兄弟节点,这里只有一个右边的兄弟节点
- 合并完后,P19的12移动到P17中,P19删除掉
- P14中删除掉指向P19的节点
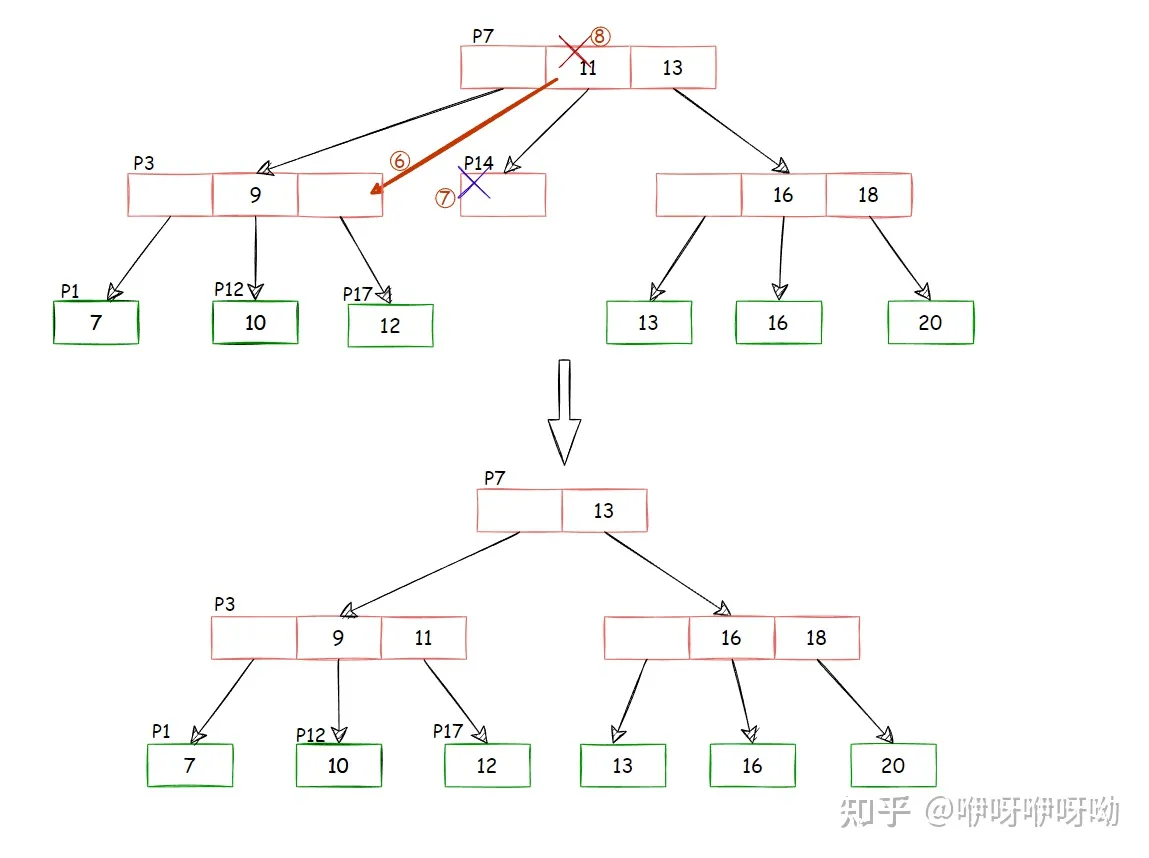
- 此时P14处于underfill状态,需要merge(为了举例子暂不考虑redistribute),将P14合并到P3(见下图)
- P7中的parent key移动到P3
- 删除P14
- 删除P7的指向P14的index
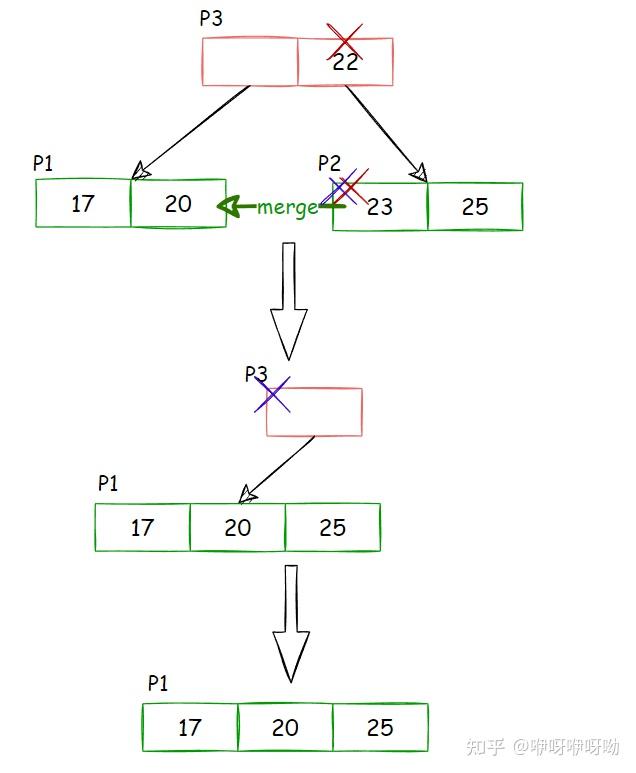
这里有一个特殊情况就是可能会造成root节点的删除(此时的策略是leaf node merge)
- 删除P2的23这个节点,P2处于underfill状态
- P2合并到P1,删除P2
- 在P3中删除指向P2的index
- root节点处于underfill状态,删除掉
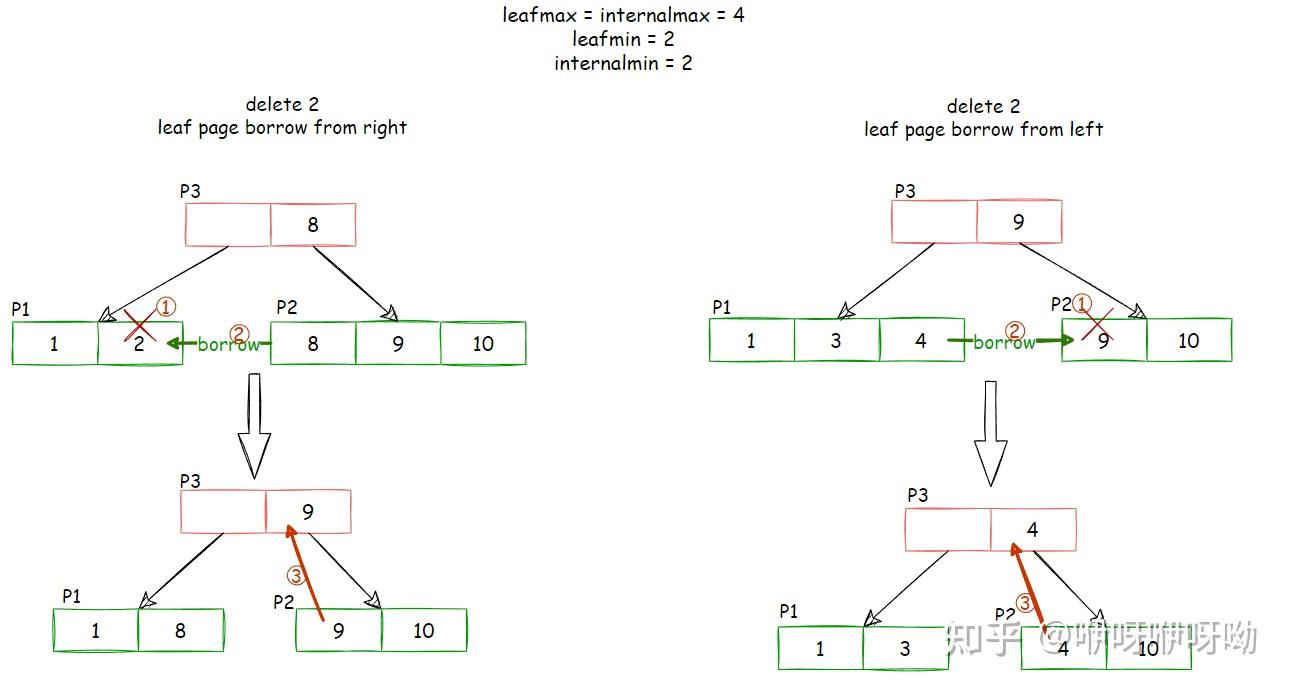
Leaf Node Redistribute
- P1中删除2
- 触发重新分配
- 重新分配完成后,为了能够区分两个child,需要更改parent key
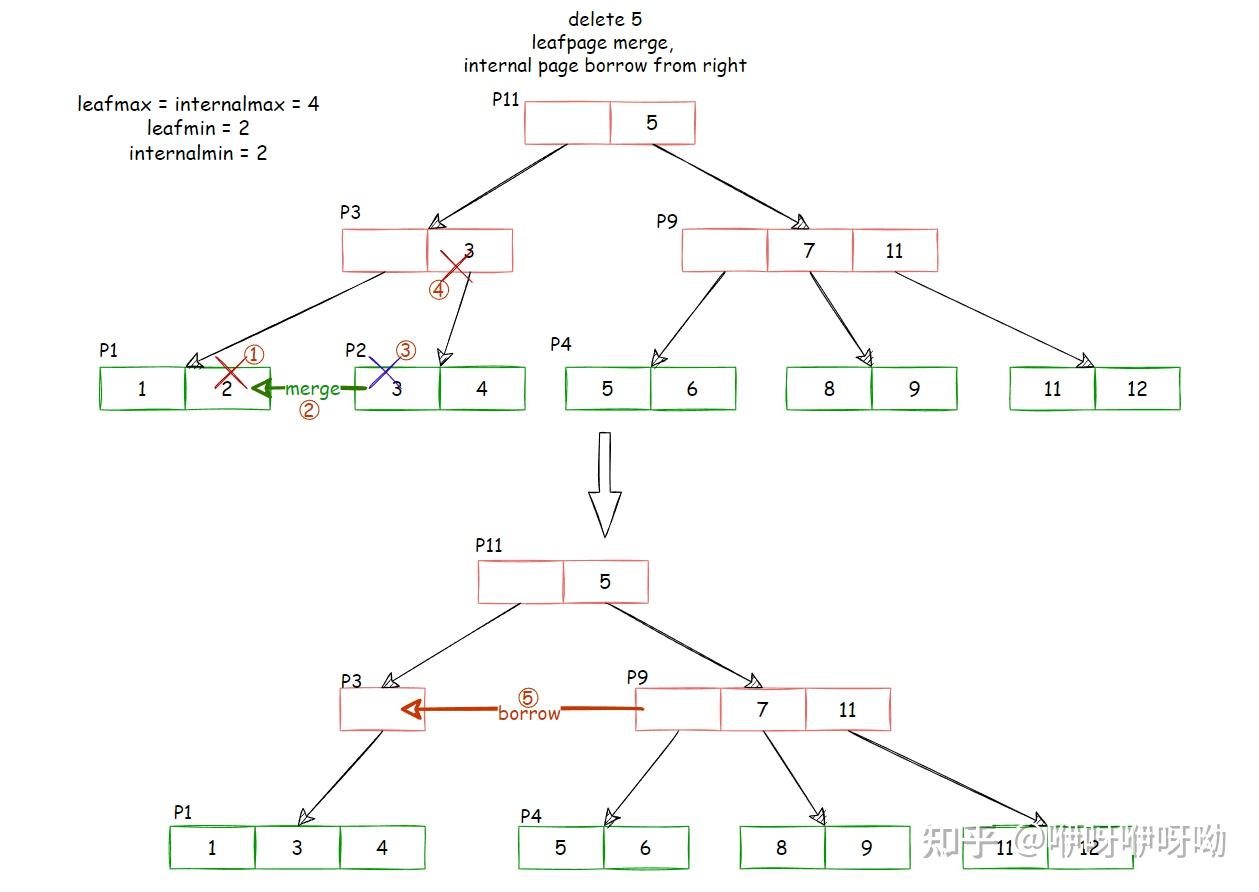
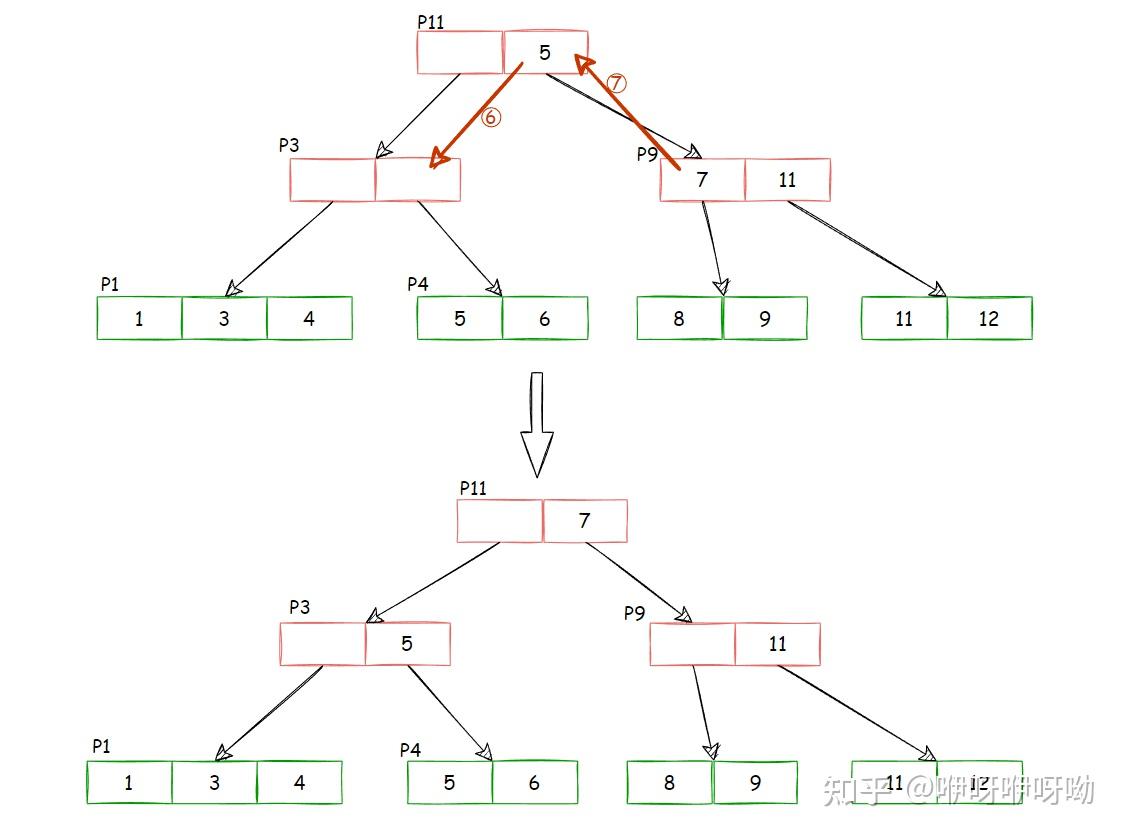
NonLeaf Node Redistribute
- 从P1中删除2
- 需要和P2进行merge(leaf node merge策略)
- 删除掉P2
- 在P3中删除掉指向P2的index
- P3处于underfill状态,需要重新分配
- 为了保持相对大小的关系不变,这里可以直接将parent key 5移动到P3
- 那么相对应的将P9中的7移动到P11
For more: