CMU445-Project1-BufferPoolManagerInstance总结
Buffer Pool
Disk-Oriented DBMS
什么是buffer pool,buffer pool有什么用(针对Disk-Oriented DBMS)
The database is all on disk, and the data in the database files is organized into pages.
In order to operate on the data the DBMS needs to bring the data into memory. It does this by having a buffer pool that manages the movement back and forth between disk and memory.
The DBMS also have an execution engine that will execute queries.
The execution engine will ask the buffer pool for a specific page, and the buffer pool will take care of bringing that page into memory and giving the execution engine a pointer to the page in memory.
The buffer pool manager will ensure that the page is there while the execution engine is operating on that memory.
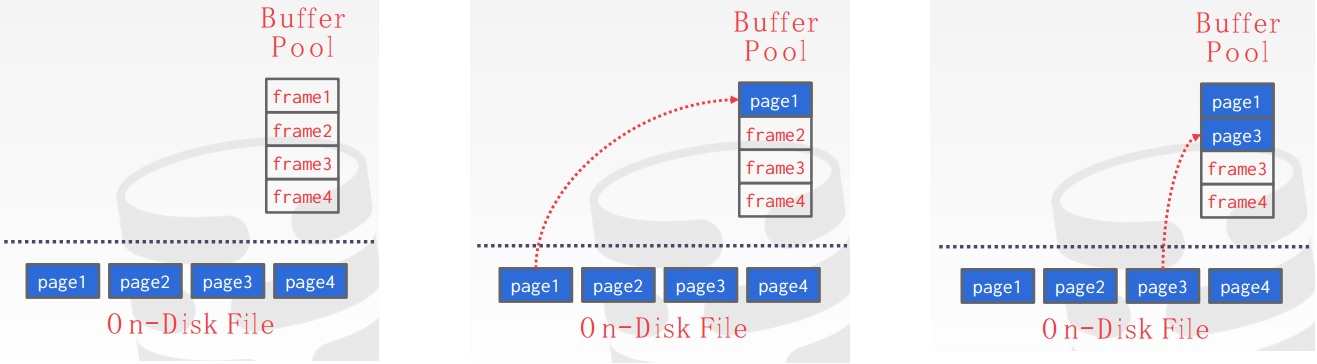
Buffer Pool Organization
buffer pool是如何利用内存的,组织数据的方式
- Memory region organized as an array of fixed-size pages.An array entry is called a frame.
- When the DBMS requests a page, an exact copy is placed into one of these frames.
Meta-data maintained by the buffer pool
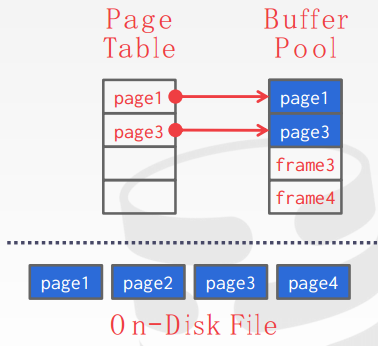
Page Table
In-memory page table (hash table) that keeps track of pages that are currently in memory. It maps page ids to frame locations in the buffer pool.
其实就是为了根据page id快速找到对应的page data,还可以判断page id对应的数据有没有在buffer pool
Dirty Flag
- Threads set this flag when it modifies a page.
- This indicates to storage manager that the page must be written back to disk.
- 其实就是判断page data有没有被修改过,如果修改过在某个时候需要将修改写回到磁盘
Pin Counter
- This tracks the number of threads that are currently accessing that page (either reading or modifying it).
A thread has to increment the counter before they access the page.
If a page’s count is greater than zero, then the storage manager is not allowed to evict that page from memory.
Structure
- buffer pool:
BufferPoolManagerInstance,本次lab需要实现的部分 - 磁盘读写相关:
DiskManager,已经提供,不需要实现 class Page- Each
Pageobject contains a block of memory that theDiskManagerwill use as a location to copy the contents of a physical page that it reads from disk. 将磁盘中内容读到内存中,放到page对象中 - The
BufferPoolManagerInstancewill reuse the samePageobject to store data as it moves back and forth to disk. This means that the samePageobject may contain a different physical page throughout the life of the system. 重复利用page object,所以page object里面的内容不是固定不变的 - The
Pageobject’s identifer (page_id) keeps track of what physical page it contains. page_id代表了里面的数据对应哪个phusical page - page具体内容存放在
data_,metadata对应上面提到的两个is_dirty_,pin_count_
- Each
page table:使用自己实现的
ExtendibleHashTable类,mapspage_idtoframe_idbuffer pool满了如何evict page:使用LRU-K算法,对应自己实现的
LRUKReplacer
Buffer Pool Manager Instance
size_t pool_size_代表了buffer pool中能容纳多少个fixed-size pagePage *pages_代表了buffer pool中的page,其大小是固定的pages_ = new Page[pool_size_];代表一开始buffer pool有多少个空的page。其实就是下面这个东西,通过frame_id索引到某个page obejctstd::list<frame_id_t> free_list_代表有哪些frame_id对应的page object还可以用来存放从磁盘中读取到的page,首先从这里拿,如果free_list满了,代表buffer page中没有多余的空间了,需要evict page到disk从而reuse page承载新的内容(如果可以)ExtendibleHashTable<page_id_t, frame_id_t> *page_table_,根据pageid可以拿到frame_id,`pages[frame_id]`可以拿到buffer pool中的某个page
Notes
NewPageImp和FetchPageImp从free_list或者LRUKReplacer拿到一个page后:- 如果page是dirty,需要先将其内容写回到disk,ResetMemory,pin_count需要置为0,is_dirty需要置为false
- 需要
pin_count++ - 将该page_id从page_table中移除
- 更新page_id(NewPage是新创建一个,FetchPage是传入page_id)
- 将page_id和frame_id对应关系存到page_table
- 调用replacer的SetEvictable和RecordAccess
这里其实可以更细化,比如如果是从free_list中拿的,可以不校验dirty,因为只有在
DeletePgImp方法中才将frame_id放到free_list,放之前已经将其对应的memory和metadata清空。FetchPageImp需要先判断pageid对应的数据有没有已经在page table,如果在代表数据在buffer pool已经有了,不需要从disk中拿,直接返回`pages[frame_id]即可。返回前需要pin_count++`并调用replacer的SetEvictable和RecordAccess。UnpinPgImp传入的dirty代表是否改变dirty flag,如果是false代表维持当前page的dirty flag,所以这里需要if判断一下才赋值FlushPgImp记得将对应的page的dirty flag置为falseDeletePgImp需要将对应page_id从page table,replacer中移除。需要Reset Memory和metadata。- 从上面可以看出,很多地方需要reset page,所以这里可以抽出一个方法,避免忘记初始化某个东西。